Webhooks
The Centra Webhook plugin lets you create webhooks for specific events whenever data changes in Centra, so you’re notified and can fetch data only when it’s actually added or updated. Centra also offers an event system through the Integration API. Using events provides more control and flexibility compared to webhooks.
How do webhooks work in Centra
Webhooks in Centra are triggered by events. An event is any change happening in Centra - a new order comes in, a product description is changed or a new product displays are added to a category. If your webhook plugin is active and registers to those types of events (Order, Product, Category), Centra will generate an appropriate webhook and send it to your URL defined in the plugin. Different webhook plugins can be used to handle different functions, and be used by separate integrations.
This is why, in addition to relying on webhooks to fetch resources from Centra only when necessary, you should also build a "fetch everything" function meant to restore the data after a network or application failure. After the data is synced, you can switch back to only fetching new or updated resources when receiving webhooks.
Versions
Storefront API
Types
Storefront API webhooks currently support events of the following types:
- Display Items (
DisplayItems): when product data is modified, such as stock, descriptions or variant changes, contains ID for each Product Display Item ID. - Categories (
Categories): when category data is modified, contains ID for each Category ID. - Pricelists (
Pricelists): when pricelist or shipping data is modified, contains ID for each Pricelist ID. - Markets (
Markets): when market data is modified, contains ID for each Market ID. - Collections (
Collections): when collection data is modified, contains ID for each Collection ID. - Brand (
Brands): when brand data is modified, contains ID for each Brand ID. - Languages (
Languages): when language data is modified, contains ID for each Language ID. - Campaign sites (
CampaignSites): when campaign sites data is modified, contains ID for each Campaign Site ID. - Affiliates (
Affiliates): when affiliate data is modified, contains ID for each Affiliate ID. - Brick and mortars (
BrickAndMortars): when Brick and Mortar data is modified, contains ID for each Brick and Mortar ID.
Data in the Storefront API is cached and it will only send a webhook once the data is in the cache. Using Integration API webhooks to fetch data from Storefront API will lead to errors as the data may not yet have been updated.
Triggers
Cache updates are triggered by the following internal event types. The key insight is that some events cascade to multiple data types.
| Internal event | Cache invalidated for |
|---|---|
AFFILIATE_EVENT | Affiliates |
ATTRIBUTE_EVENT | Categories, DisplayItems |
BRAND_EVENT | Brands, DisplayItems |
BRICK_AND_MORTAR_EVENT | BrickAndMortars |
CAMPAIGN_SITE_EVENT | CampaignSites |
CATEGORY_EVENT | Categories, DisplayItems |
COLLECTION_EVENT | Collections |
DISPLAY_EVENT | DisplayItems |
DISPLAY_ITEM_EVENT | DisplayItems |
DISPLAY_RELATION_EVENT | DisplayItems |
DISPLAY_REMOVED_EVENT | DisplayItems |
LANGUAGE_EVENT | Languages |
LOWEST_PRICE_EVENT | DisplayItems |
MARKET_EVENT | DisplayItems, Markets |
MARKET_PRODUCTS_EVENT | DisplayItems |
MEASUREMENT_CHART_EVENT | DisplayItems |
PRICELIST_EVENT | Pricelists |
PRODUCT_EVENT | DisplayItems |
PRODUCT_MEDIA | DisplayItems |
SHIPPING_EVENT | Pricelists |
STOCK_EVENT | DisplayItems |
STORE_ITEM_EVENT | DisplayItems |
VARIANT_EVENT | DisplayItems |
For events triggering cascading invalidation, it only triggers it for related entities. E.g. ATTRIBUTE_EVENT will trigger invalidation of DisplayItems and Categories where that attribute is exposed.
Payload
Triggered when a brand connected to multiple products is updated.
{
"Brands": ["7"],
"DisplayItems": ["10123", "10124", "10125"]
}
Important webhook behaviors
- Not guaranteed in order - Webhooks may arrive out of sequence. Handle duplicate/old data gracefully.
- Not guaranteed to arrive - Network issues may prevent delivery. Always have a fallback mechanism.
- May be duplicated - The same event might trigger multiple webhooks. Use idempotent processing.
- Fire after cache updates - Your API will return updated data immediately when you query it.
- Large payloads chunked - If many IDs changed, payload is split into multiple HTTP requests.
- Async delivery - Webhooks don't block cache updates. Delivery may take a few seconds.
Integration API
Integration API webhooks currently support events of the following types:
- Order (
order): When order data is modified,idis the Order ID. - Shipment (
shipment): When shipment data is modified,idis the Shipment ID. - Customer (
customer): When customer data is modified,idis the Customer ID. For B2C only, in B2B, accounts are sent instead of customers. - Account (
account): When account data is modified,idis the Account ID. Only triggers for B2B. - Check first (
check_first): When order check first changes status,idis the order number. - Allocation request (
allocation_request): When order allocated from "Direct, then confirm" changes status,idis Allocation request ID. - Return (
return): When return is created, updated or deleted,idis the Return ID.
New order created:
{
"events": [
{
"type": "order",
"action": "insert",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:40:48.735992",
"id": 78
}
]
}
If you are also getting customer web hooks and it is a new customer:
{
"events": [
{
"type": "customer",
"action": "insert",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:37:25.753541",
"id": 20
},
{
"type": "order",
"action": "insert",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:37:25.754834",
"id": 78
}
]
}
Confirming order:
{
"events": [
{
"type": "order",
"action": "update",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:44:00.488430",
"id": 78
}
]
}
Expedite order and Create Shipment:
When creating a shipment you will also get an “action": "update" on order as the status will be updated from confirmed to processing, while the shipments action is create.
{
"events": [
{
"type": "shipment",
"action": "create",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:48:36.845079",
"id": 1137
},
{
"type": "order",
"action": "update",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:48:36.845869",
"id": 78
}
]
}
Shipment “Good to Go”
{
"events": [
{
"type": "shipment",
"action": "good_to_go",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:53:51.392528",
"id": 1137
}
]
}
Shipment marked as Paid
{
"events": [
{
"type": "shipment",
"action": "update",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:55:16.360515",
"id": 1137
},
{
"type": "order",
"action": "update",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:55:16.360864",
"id": 78
}
]
}
Shipment info added and shipment completed
Now the shipment has been updated and completed. The order status has changed to Completed, as shown in the action field.
{
"events": [
{
"type": "shipment",
"action": "complete",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:57:39.143979",
"id": 1137
},
{
"type": "order",
"action": "update",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:57:39.144447",
"id": 78
},
{
"type": "shipment",
"action": "update",
"date": "2025-01-24 09:57:39.144635",
"id": 1137
}
]
}
Reset Password
Integration API also includes a webhook for triggering forgotten passwords, but for the flow to work you need some additional steps.
- Enable the
Webhook pluginand chooseIntegration APIin the version field. - The
Forgotten passwordneeds to be triggered. This can be done either via the API or in Centra. - An additional store option has been added to mute Centra's
Forgotten passwordemail, if a mailing plugin is not used.
Example:
{
"list": {
"events": [
{
"type": "customer",
"action": "forgot_password",
"date": "2024-12-16 15:39:32.278106",
"id": 1, // customer id
"data": {
"email": "customer@example.com",
"passwordResetToken": "123456789abcde" // example token, do not rely on exact format or length
}
}
]
},
"url": "https:\/\/example.com\/webhook_endpoint"
}
Setup
You can find the Webhook plugin under Webhooks in the plugin list.
Configuration
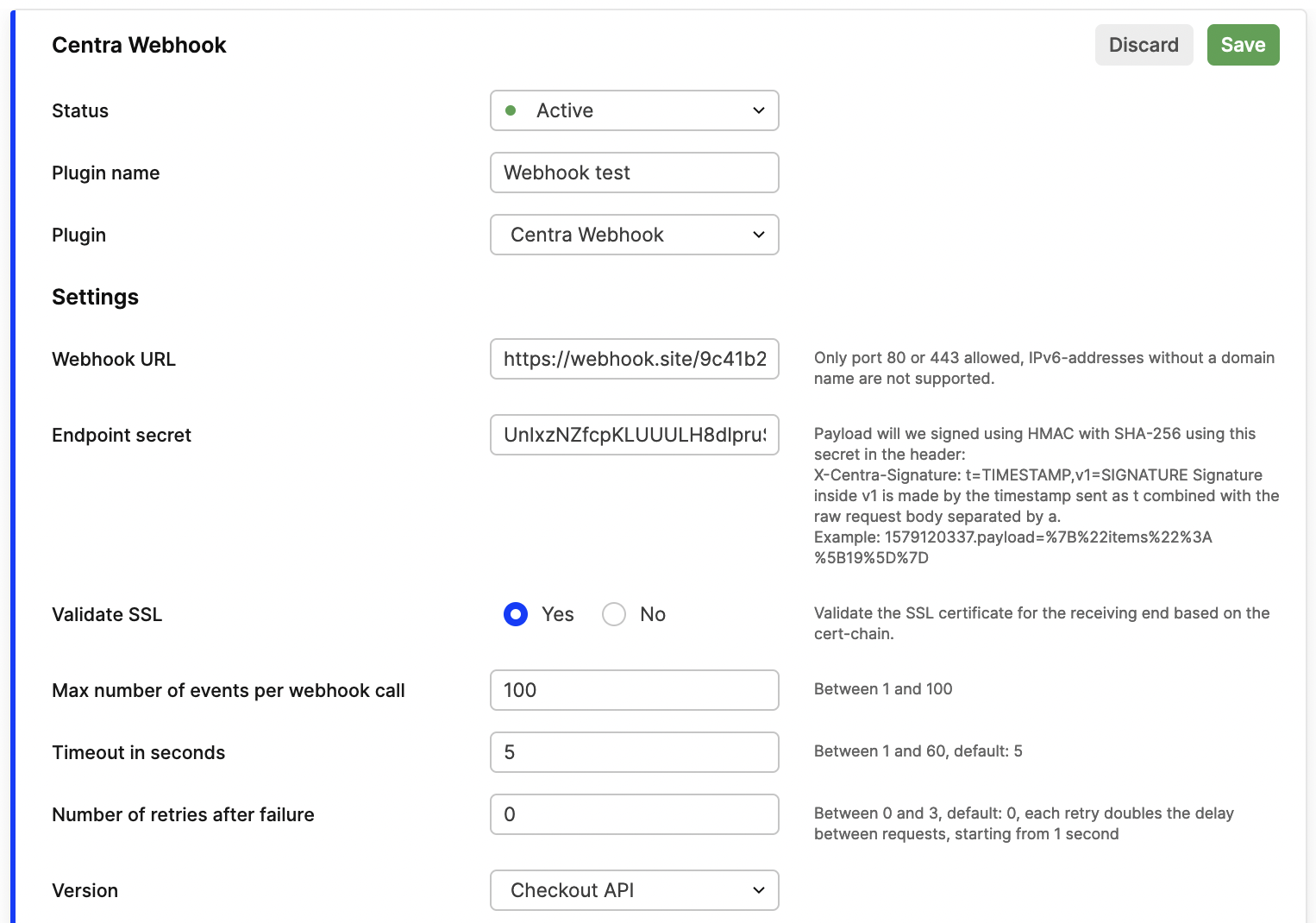
Centra sends event notifications to your external systems via webhooks using HTTP or HTTPS. Only ports 80 and 443 are supported, and IPv6 addresses without a domain name are not allowed.
Available settings
Webhook URL: The public URL where Centra should deliver webhook events.Endpoint secret: An optional shared secret used to verify that webhook requests come from Centra.Validate SSL: Enable this option if you want Centra to verify the SSL certificate of your webhook endpoint. When active, Centra checks the full certificate chain for validity.Max number of events per webhook call: Specifies how many separate Centra events can be combined into a single webhook request.
Range: 1–100, default: 100Timeout in seconds: Defines how long Centra waits for a response before timing out and aborting the delivery.
Range: 1–60, default: 5Number of retries after failure: Determines how many times Centra should retry sending a webhook if a delivery fails. Each retry doubles the delay between attempts, starting from 1 second.
Range: 0–3, default: 0Version: Specifies which API version (and event taxonomy) the webhook follows. Each version provides a different set of event triggers depending on your integration needs.Storefront APIIntegration API
Event triggers: List with available event triggers. We will only send webhook notifications for the events you have subscribed to. For each event trigger there's aField Name, this is the key used in the payload.
Recommended settings
Max number of events per webhook call: 10Timeout in seconds: 5Number of retries after failure: 2
This configuration offers a reliable balance between performance, delivery speed, and fault tolerance for most webhook integrations.
Format
A webhook is sent as a regular POST-request using a urlencoded payload-parameter containing the JSON:
POST /url HTTP/1.1 Host: example.com X-Centra-Signature: t=15798... Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded payload=%7B%22products%22%3A...
The format of the webhook:
{ "products": ["52"], "categories": ["14", "16"], "anotherType": ["1"] }
A webhook can send multiple updates for multiple types at the same time. It will always send an array of ID for each type. The key inside the JSON correlates with the "Field Name" in each event trigger in the webhook set up to receive.
Some modifications in Centra will trigger multiple types at the same time. If you for example sort products inside a category, when the new order is saved, the webhook will contain both the products that got their sorting changed, but also the category the sorting was changed in, like this:
{ "products": ["1", "6", "7"], "categories": ["1"] }
This allows you to write logic in your end depending on how you cache your data. In this case, you might want to recache the whole category, by fetching all products inside the category:
curl -X POST -H "Content-type: application/json" \ -d '{"categories":["1"]}' \ "https://example.centra.com/api/checkout/products"
Security
To ensure webhooks come from Centra, you should verify the signature in the X-Centra-Signature header.
Signature format: t={timestamp},v1={hashedPayload}
Where:
timestampis the Unix time when webhook was sent.hashedPayloadis the HMAC-SHA256 of{timestamp}.{requestBody}.
Example
timestamp: 12345678
requestBody: payload=%7B%22x%22%3A%22test%22%7D
Endpoint secret: test123
We already have timestamp, but hashedPayload needs to be calculated:
Running 12345678.payload=%7B%22x%22%3A%22test%22%7D through the hashing algorithm with secret test123 results in 0b9cd84f5d583e5e1aadfb9f160aa8080b51d5b85ff85808d6b75bdac356c549.
Our signature becomes:
X-Centra-Signature: t=12345678, v1=0b9cd84f5d583e5e1aadfb9f160aa8080b51d5b85ff85808d6b75bdac356c549
Implementation snippet
const express = require('express');
const crypto = require('crypto');
const app = express();
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
const MAX_TIMESTAMP_AGE_SECONDS = 300;
// Verify webhook signature using regex for clean parsing
function verifyWebhookSignature(payload, signature, secret) {
// Parse signature: v1,t=TIMESTAMP,hmac-sha256=HASH
const match = signature.match(/t=(\d+).*hmac-sha256=([a-f0-9]+)/);
if (!match) {
throw new Error('Invalid signature format');
}
const timestamp = parseInt(match[1], 10);
const providedHash = match[2];
// Verify timestamp is recent (prevent replay attacks)
const now = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);
if (now - timestamp > MAX_TIMESTAMP_AGE_SECONDS) {
throw new Error('Webhook timestamp too old');
}
// Compute expected signature
const signedContent = `${timestamp}.${payload}`;
const computedHash = crypto
.createHmac('sha256', secret)
.update(signedContent)
.digest('hex');
// Constant-time comparison (prevents timing attacks)
if (
!crypto.timingSafeEqual(
Buffer.from(providedHash, 'hex'),
Buffer.from(computedHash, 'hex')
)
) {
throw new Error('Invalid signature');
}
return true;
}
// Middleware: Verify webhook signature
const verifyWebhook = (req, res, next) => {
const signature = req.headers['x-centra-signature'];
if (!signature) {
return res.status(401).json({ error: 'Missing signature' });
}
try {
verifyWebhookSignature(
req.body.payload,
signature,
process.env.CENTRA_WEBHOOK_SECRET
);
next();
} catch (error) {
console.error('Signature verification failed:', error.message);
res.status(400).json({ error: 'Invalid webhook' });
}
};
app.post('/webhook/centra', verifyWebhook, async (req, res) => {
// Return immediately to Centra
res.status(200).json({ success: true });
// Process webhook asynchronously (don't block response)
processWebhook(req.body.payload).catch(err => {
console.error('Webhook processing failed:', err);
});
});
async function processWebhook(payloadString) {
try {
const webhookData = JSON.parse(payloadString);
if (!webhookData || typeof webhookData !== 'object') {
throw new Error('Invalid webhook data');
}
// Iterate over each data type that changed
for (const [dataType, ids] of Object.entries(webhookData)) {
if (ids?.length > 0) {
console.log(`${dataType} changed:`, ids);
// Invalidate cache for each affected item
for (const id of ids) {
// Cache invalidation logic goes here
// Example: await cache.delete(`${dataType}:${id}`);
}
}
}
console.log('Webhook processed successfully');
} catch (error) {
console.error('Webhook processing error:', error);
}
}
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Webhook server listening on port 3000');
});
Troubleshooting Delivery Issues
Testing with a parallel webhook plugin can help identify whether the issue lies with the sender, the webhook system or the recipient (e.g., the integration, server, or network). It's important to confirm that the webhook was sent and isolate potential problems with external systems.
Some important concepts related to their configuration and functionality:
Max Events per Webhook
This setting determines how many events are included in a single HTTP POST message. For example:
- 1 Event per Webhook: Multiple webhooks are sent, each containing only one event.
- Many Events per Webhook: Fewer webhooks are sent, but each contains multiple events.
Regardless of this setting, all events will be delivered—it's just a matter of grouping.
Retries and Timeouts
For every batch of events sent:
- Retry Attempts: We will try sending the webhook a specified number of times if it fails to reach the endpoint.
- Timeout: If the webhook is not picked up within the defined timeout period (in seconds), it is considered a failure, and a retry is attempted.
- If the retries fail repeatedly, we stop attempting to deliver that batch.
Troubleshooting Delays or Failures
If a webhook is not received:
- It's essential to check the integration or network performance on the receiving side, as delays or failures might be caused by external factors such as slow servers or network congestion.
- Testing with parallel webhook plugins can help identify whether the issue lies with the receiving system or network.
Even if a webhook is not received due to such issues, this does not mean the webhook was not sent.